

Thesis Proposal
The Petroleum and Petrochemical College
Chulalongkorn University
Thesis title :
Adsorption of surfactant on fiber paper related to paper recycling
Thesis for :
Master degree in Petrochemical Technology
Name of student : Suvena Somabutr
Student ID. Number : 4171033063
Name of advisor : Prof. J. F. Scamehorn
Name of co-advisor :
Asso. Prof. Kunchana Bunyakiat
Dr. Kitipat Siemanond
Academic year : 1998
Date of preparation : 15 March 1999
Student signature :
Approved by :
Background
Introduction
The majority of the technique of deinking process in paper recycling basically has 2 types ; flotation and washing.
This research will concentrate only on adsorption isotherm which is in part of flotation deinking process. Generally, we choose surfactants as base separation for flotation because of 3 main advantages;
Froth flotation will separate ink from fiber by adding fatty acid (eg. Oleic acid). Calcium ion is added as an activator for helping adsorption mechanism, then air is sprayed through the solution. The dissolved material adheres to the adsorbed surfactant layer around the air bubbles and is carried up to the foam at the surface of the liquid. The last step is skim bubble off, the ink particle also detach from the paper, as shown in the figure below.
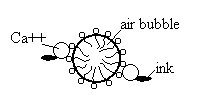
At the right condition, the good micelle will form on the ink. The controlled parameters are pH, type and concentration of surfactant, point of zero charge (pzc) and zeta potential.
Literature survey
In addition to washing process, flotation deinking is used for paper recycling. M. Rutland, R. J. Pugh [3] studied mechanism of surfactant and calcium in adsorption by surface force and coagulation technique. The surface force technique concerns the interaction of fatty acid flotation collectors and calcium activator with a negative charged mica substrate at high pH. Since the surface of ink particle is enriched by negatively charged group.
This result implies that under alkaline condition, it can be concluded by 3 ideas, shown in the figure below, which are

After that the improvement of technique to enhance efficiency of process is discovered. Loreen D. Ferguson [2] studied deinking chemicals for support deinking paper recycling.
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) : used to adjust pH, sponify or hydrolyze the ink resin. The alkaline environment is often reported to swell the fibers. The pH conventionally used for pulping is 9.5 - 11.0 and fiber will be more flexible. The amount of caustic soda and others added on system should be custom optimized for maximum performance. Adding NaOH on wood-containing cause alkali darkening. The alkalinity have affected on brightness afer pulping and flotation deinking.
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) : used to decolorize the chromophores generated by the alkaline pH in wood-containing pulper.
H2O2 + NaOH Û HOO- + Na+ + H2O
at pH of 10.0 - 11.5 and Temperature of 40 - 80OC
HOO- (perhydroxyl anion) is used as the active bleaching agent. The best use of peroxide is to maximize HOO- and control important factors such as raise pH, raise temperature, reduce side reaction by reducing heavy metal ion, increase peroxide concentration. The decomposition of peroxide can be reduced by adding of stabilization agents such as chelats and sodium silicate.
Chelating agents : such as DTPA diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid, EDTA ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) Chelant is used to form soluble complex with heavy metal ions. But DTPA and EDTA in some country are banned because effluent stream into the aquatic will harm aquatic life.
Sodium Silicate (Na2SiO3) : or water glass is used as a 41.6O Baume solution of sodium metasilicate which contain equally of SiO2 and Na2O. Alkalinity about 11% NaOH. Silicate, is often referred to a peroxide stabilizer, are formed by a colloidal structure with the heavy metal ions and aids in deinking by preventing the ink from redepositing on the fiber surface. It is most widely used in laundry soap. The sodium silicate solution is a source of alkalinity derived from hydroxyl group as well as a pH buffering agent.
Na2SiO3 + H2O Û 2Na+ + OH- + HSiO3
The other quality of sodium silicate is help more brightness but it cause scaling, fouling.
R. N. RAO and P. Stenius [4] who found A model printed of dry ink has 3 layers: primary, secondary and tertiary layer. Mechanical force in flotation alone cannot successfully remove primary ink layer in direct contact with fiber. Then adding of surfactant will help to soften the ink and affect the ink/fiber interaction, complete release ink will occur. The surfactant that is used in experimental is mostly fatty acid (eg. Oligoethylene-oxide alkyl ether surfactant) and calcium soap. Calcium soap is helped to remove ink by precipitation, agglomerate and attach to air bubble.
In the experiment any type of force (detachment of ink without shear force, with shear force, mechanical shaking) is applied to help deinking. The 100 percent release ink was achieve by both mechanical actions and at high surfactant concentration with each surfactant.
New technique for deinking of Wayne F. Carr [5] is take experiment in removing difficult-to-disperse ink in waste paper. Conventional deinking process of washing and flotation are not very effective at reclaiming speck-free-fiber.
Characteristics of the contaminant
Ink have traditionally consisted of colored pigments for transporting fluidity. Some modern inks consist of fine pellets fixed by fusion. Approaching to ink binder (toner) removal undertaken during the past few years can be group into 2 catagories.
Trend in new system design
Reference
Objectives
Scope of Research Work
This thesis research work focuses on the adsorption of surfactants and calcium on fiber paper at equilibrium. The data from experiment will be ploted to analyze the adsorption isotherms of surfactants on fiber paper. The objective of work is to understand the perspective on the importance of understanding the adsorption mechanism of surfactant and calcium in flotation deinking.
This thesis will find the proper type of surfactants for adsorption on fiber paper. Then sodium dodecyl sulphate and sodium octanoate are studied in model plant. The activator, Ca2+ from calcium chloride is used for helping adsorption. The pH condition in the experiment will be varied by sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
Methodology
Design and experimental setup
The equilibrium between surfactants and calcium will be studied in test tubes.
Method for preparing surfactant (SDS, C8)
The second step (reprecipitate surfactant by using methanol)
Method for prepare fiber [1]
Method for obtained adsorption isotherm (solution depletion method)
Experimental procedures
Controlled parameters
The surface area of fiber must be the same in each batch. The type of paper must be the same. The concentration of calcium from paper must be less than 0.1 ppm.
Variable parameters
The variable parameter is pH value and type of surfactant which vary in this research to study the adsorbed concentration of surfactant versus equilibrium surfactant on fiber.
Methods of chemical analysis and measurement
The concentration of sodium octanoate (C8) adsorb on fiber paper is detected by total organic carbon analyzer. The concentration of sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS) adsorb on fiber paper is detected by HPLC. The concentration of Ca2+ adsorb on fiber paper is detected by AAS.
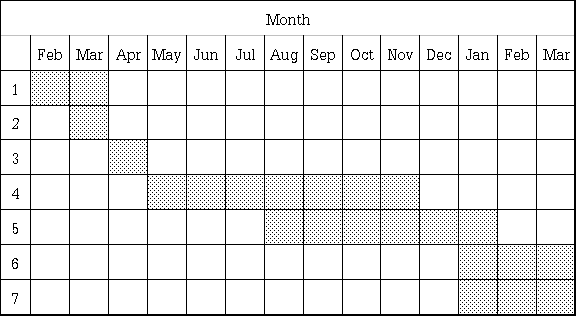
Sequence of Research Activities
Time Table
year : 1999
Budget
Chemicals Total
Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate (SDS) 9,000.00
Sodium Octanoate (C8) 9,000.00
Office paper (Xerox 4200 DP 20lb.) 2,000.00
CaCl2 1,000.00
NaOH 1,000.00
Methanol 1,000.00
Equipment Total
Filter Paper 3,000.00
Equipment fee at Ministry of science 4,000.00
Total 26,000.00